Connective Tissue
Types of Fibres
- Collagen Fibres
- Long wavy bundle of Fibres
- Not branching
- Seen in bone, Cartilage, Tendon, and Ligament giving strength to structures.
- Elastic Fibres
- Short
- Straight
- Single
- Branching
- Reticular Fibres
- This is a type three collagen Fibres.
- Network of Fibres Giving framework which can be seen in organs like lymphoid organs ( Liver, Spleen, Lymph nodes).
Types of Connective Tissue
- Loose connective tissue
- Fibers create loose, open frameworks.
- Areolar tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Reticular tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Fibers are densely packed.
- Dense regular tissue.
- Dense Irregular tissue.
- Elastic tissue.
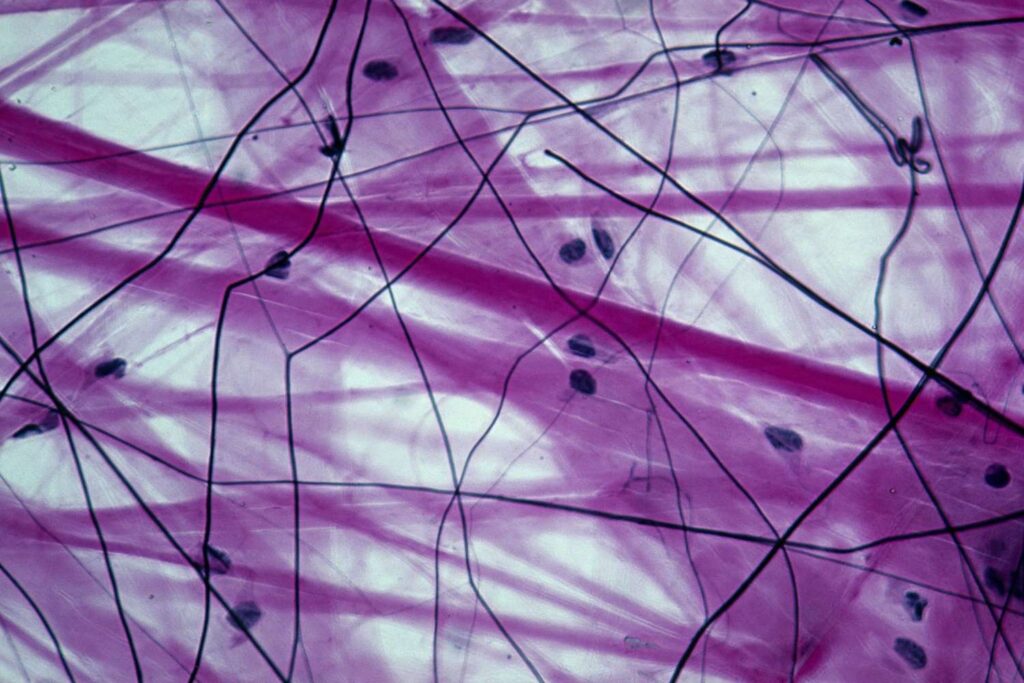
1. Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
- Has less collagen fibers.
- More in cells like Fibrocytes, Macrophages, Mast Cell.
- Ex: Sub-epithelial connective tissue: Lamina propia.
- Other Fibers like elastic fibers are also present.
2. Reticular Loose Connective Tissue
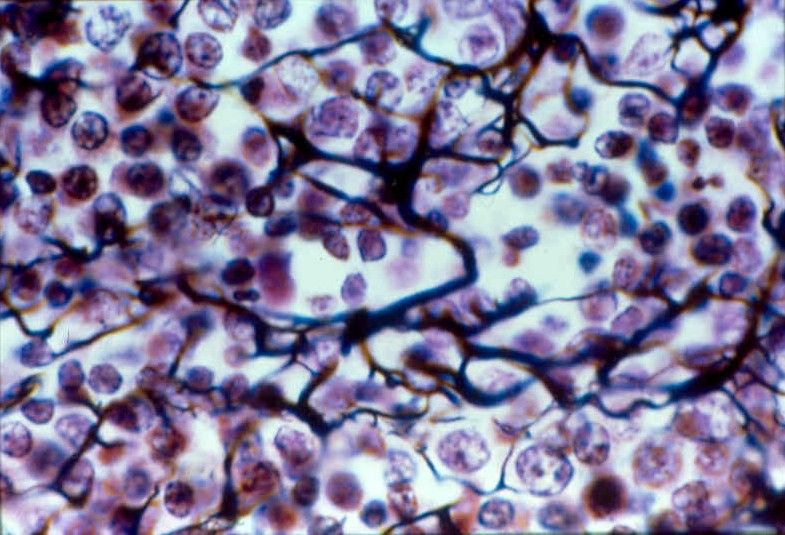
Location : mainly lymphatic organs
- Liver
- Spleen
- Lymph Nodes
- Bone Marrow
- Kidney
Exception :
Reticular Loose Connective Tissue is not present in Thymus which is also a lymphoid Organ.
- Shorter branching fibers are present.
- Providing Supporting Frameworks.
3. Dense Regular Connective Tissue
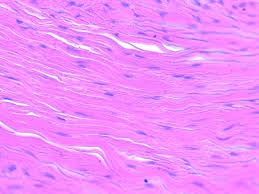
- Has more and dense collagen fibers.
- Collagen Fibers run parallel to each other in a regular fashion.
- Found in:
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Aponeurosis (Flat Tendon).
- Bundles of collagen fibers are regular and parallel to each other.
4. Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
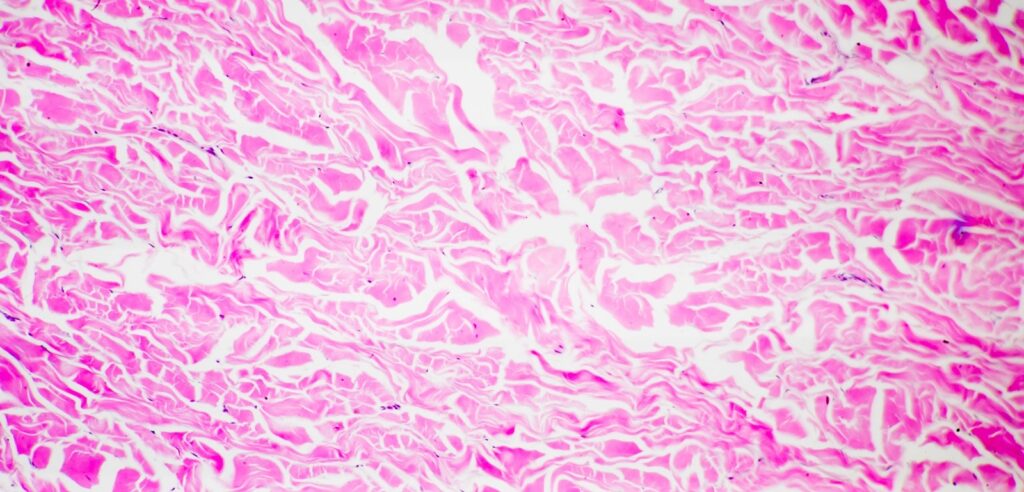
- Collagen Fibers are present.
- Do not run parallel to each other.
- Hence, called Irregular connective tissue.
- Location:
- Capsules of visceral organs.
- Periosteum and Perichondrium.
- Nerve and Muscle Sheaths.
- Deep Reticular layer of Dermis.
Leave a Reply